
What is the Common AI Assessment?
What is the Common AI Assessment?
Risk-minded organizations are in a tough spot. While AI has tremendous potential, it presents sizable security, privacy, legal, and ethical risks. Yet AI adoption is accelerating, with 77% of SaaS companies building or launching AI features in 2023. (source)
How do you know if rapidly evolving vendor AI systems are safe and trustworthy? For organizations with hundreds or thousands of vendors, it's hard to collect data fast enough to keep up.
About
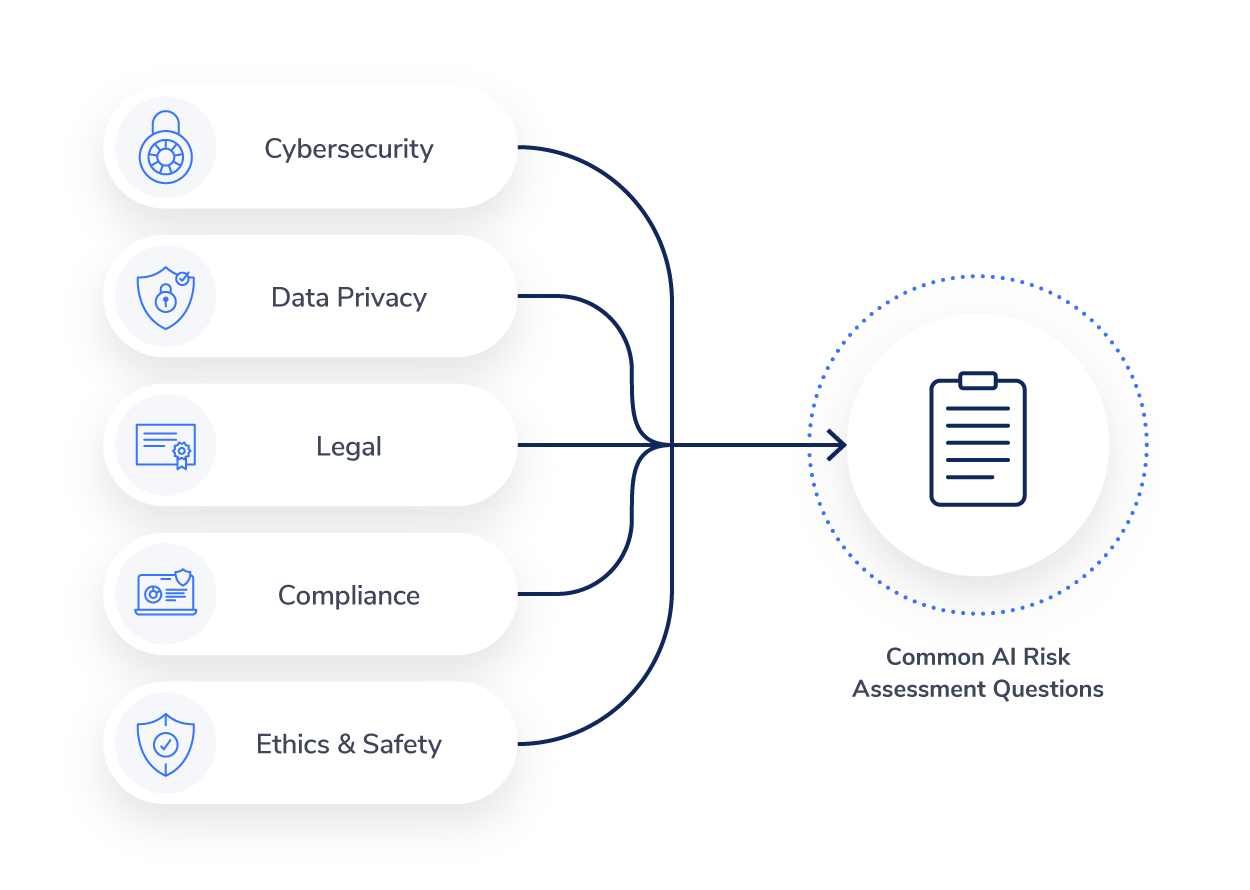
The vast majority of vendor AI risk assessments start with the same questions.
The Common AI Risk Assessment consolidates the top questions that risk experts are asking about vendor AI systems. It reflects market feedback on transparency and disclosure requirements for trustworthy AI.
By making answers to these key questions readily available, risk leaders can quickly understand the risk posture of vendor AI systems and identify systems that warrant deeper due diligence.
A starting point - not a standard.
These questions are already being asked today. Customer-side Vendor Risk teams and vendor-side Customer Trust & Assurance teams are both fielding a significant increase in the volume of AI due diligence questions. That volume is expected to increase dramatically into 2025 and beyond.
The goal of the Common AI Risk Assessment is to make it easier for organizations to exchange this information. It will evolve with market expectations to help vendors and customers stay aligned as AI risks and regulation emerge.
How do the questions get answered?
Gen AI Trust Network populates answers to the Common AI Risk Assessment through a combination of public disclosure data and vendor self-attestations.
Gen AI Trust Network continuously scans public domains to answer as many questions as possible based on what vendors already share in binding disclosures. However, our research shows that fewer than 20% of vendors with AI disclose it in their Terms of Service.
Vendors can take a proactive stance on responsible AI disclosure through three simple steps:
- Completing a self-attestation
- Hosting this artifact in their Trust Portal
- Authorizing Gen AI Trust Network to access this artifact
Vendor AI Transparency values indicate completeness of disclosure against the Assessment questions - not the risk of the underlying disclosure itself.
Answers provided through self-attestation are made available to customers at the vendor’s authorization.

Are you a vendor?
If you are a vendor and want to be proactive on responsible AI disclosure, please reach out! No matter whether or not you have implemented AI systems, your customers need this information for their external AI risk inventory for compliance.
Contact us